[toc]
8-Linux-管理-2
一、设置主机名
命令:hostname
显示或设置主机名。
1、临时设置
命令:hostname 主机名
[root@localhost ~]# hostname tiger
[root@localhost ~]# su
[root@tiger ~]#
不需要重启,但需要切换用户例之生效。重启后则还原主机名。
2、永久设置
2.1、使用hostnamectl命令设置
与以前版本不同的是,centos7提供了hostnamectl命令来操作主机名。
查看主机名
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl
Static hostname: localhost.localdomain
Icon name: computer-vm
Chassis: vm
Machine ID: ea108dce8b7946b29a33837c2ba73f03
Boot ID: 2c958ed6666941128913eb4b96146e68
Virtualization: vmware
Operating System: CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
CPE OS Name: cpe:/o:centos:centos:7
Kernel: Linux 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64
Architecture: x86-64
设置主机名
命令:hostnamectl set-hostname 主机名
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname tiger
[root@localhost ~]# su
[root@tiger ~]# hostnamectl
Static hostname: tiger
Icon name: computer-vm
Chassis: vm
Machine ID: ea108dce8b7946b29a33837c2ba73f03
Boot ID: 2c958ed6666941128913eb4b96146e68
Virtualization: vmware
Operating System: CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
CPE OS Name: cpe:/o:centos:centos:7
Kernel: Linux 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64
Architecture: x86-64
2.2、修改/etc/hostname文件直接设置
[root@tiger ~]# vim /etc/hostname
tiger
:wq
直接修改文件设置后,需要重启电脑才能生效。
二、服务管理
centos7以前使用chkconfig命令对服务进行管理。简单说,chkconfig类似于windows下安全辅助工具,提供对开机启动项的管理服务。
centos7后使用使用systemd替换了SysV。Systemd目的是要取代Unix时代以来一直在使用的init系统,兼容SysV和LSB的启动脚本,而且够在进程启动过程中更有效地引导加载服务。
systemctl是systemd服务中管理服务的工具。可以认为systemctl命令将service和chkconfig命令结合在了一起。
在前面已经针对服务的启动、重启、停止、重载、查看状态等常用的命令讲过,这里针对服务的开机启动管理进行讲解
1、查看所有运行中服务的单元
命令:systemctl list-units --type=service --all
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl list-units --type=service --all
UNIT LOAD ACTIVE SUB DESCRIPTION
abrt-ccpp.service loaded active exited Install ABRT coredump hook
abrt-oops.service loaded active running ABRT kernel log watcher
abrt-vmcore.service loaded inactive dead Harvest vmcores for ABRT
abrt-xorg.service loaded inactive dead ABRT Xorg log watcher
abrtd.service loaded active running ABRT Automated Bug Reporting Tool
………………省略部分输出………………
2、查看所有安装的服务单元(包含未启动)的状态
命令:systemctl list-unit-files --type=service --all
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl list-unit-files --type=service --all
UNIT FILE STATE
abrt-oops.service enabled
abrt-pstoreoops.service disabled
alsa-restore.service static
saned@.service indirect
………………省略部分输出………………
其中state主要的状态值说明:
static:服务开机启动项不可被管理enbaled:服务开机启动disabled:服务开机不启动indirect:服务关闭
3、设置服务开机启动
命令:systemctl enable 服务名目标
示例1:设置sshd.socket开机自动启动
① 查看是否开机启动
命令:systemctl list-unit-files |grep sshd.socket
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl list-unit-files |grep sshd.socket
sshd.socket disabled
② 设置开机自动启动
命令:systemctl enable sshd.socket
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable sshd.socket
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/sockets.target.wants/sshd.socket to /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.socket.
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl list-unit-files |grep sshd.socket
sshd.socket enabled
4、关闭服务开机启动
命令:systemctl disable 服务名目标
示例1:设置sshd.socket开机不启动
命令:systemctl disable sshd.socket
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl disable sshd.socket
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/sockets.target.wants/sshd.socket.
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl list-unit-files |grep sshd.socket
sshd.socket disabled
三、ntp服务
作用:ntp主要是用于对计算机的时间同步管理操作。
1、安装服务
1.1、使用rpm命令查看是否安装ntp服务
rpm是一个强大的命令行驱动的软件包管理工具,用来安装、卸载、校验、查询和更新Linux系统上的软件包。
命令:rpm -eq ntp
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -eq ntp
ntp-4.2.6p5-29.el7.centos.2.x86_64
centos7已经默认安装的ntp服务,如果使用的linux系统没有安装ntp服务,可以过过yum命令进行安装。
1.2、使用yum命令安装ntp服务
命令:yum -y install ntp
安装完成,可将服务设为开机启动
命令:systemctl enable ntpd
2、使用ntpdate命令同步时间
同步服务器时间方式有两种:
- 手动同步时间
- 通过服务自动同步
2.1、手动同步时间
命令:ntpdate 服务器地址
ntp时间服务器地址:【http://www.ntp.org.cn/pool】
[root@localhost ~]# date -s "2000-01-01" #设置错误时间
2000年 01月 01日 星期六 00:00:00 CST
[root@localhost ~]# ntpdate 120.25.108.11 #手动同步时间
20 Feb 13:57:32 ntpdate[64350]: step time server 120.25.108.11 offset 667144621.657366 sec
[root@localhost ~]# date
2021年 02月 20日 星期六 13:57:40 CST
2.2、设置时间自动同步服务
服务名:netpd 对应的目标为ntpd.service
① 查看ntpd服务是否启动
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl status ntpd
● ntpd.service - Network Time Service
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/ntpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: inactive (dead) # 停止状态
② 设置错误时间
[root@localhost ~]# date -s "2000-01-01"
2000年 01月 01日 星期六 00:00:00 CST
③ 启动ntpd服务
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start ntpd
④ 再次查看时间
[root@localhost ~]# date
2021年 02月 20日 星期六 14:01:26 CST
结果已同步时间
⑤ 将ntpd加入开机启动,同时开启ntpdate服务开机校验时间服务
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable ntpd
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/ntpd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/ntpd.service.
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable ntpdate
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/ntpdate.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/ntpdate.service.
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl list-unit-files | grep ntpd
ntpd.service enabled
ntpdate.service enabled
四、防火墙
1、简介
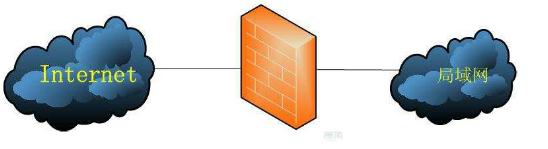
防火墙的作用是保障数据的安全性。
防火墙作为公网与内网之间的保护屏障,在保障数据的安全性方面起着至关重要的作用。
防火墙虽有软件或硬件之分,但主要功能都是依据策略对穿越防火墙自身的流量进行过滤。防火墙策略可以基于流量的源目地址、端口号、协议、应用等信息来定制,然后防火墙使用预先定制的策略规则监控出入的流量,若流量与某一条策略规则相匹配,则执行相应的处理,反之则丢弃。这样一来,就可以保证仅有合法的流量在企业内网和外部公网之间流动了。
2、防火墙管理工具
centos7以前的版本中,使用iptables来管理防火墙策略。
在centor7中,firewalld防火墙取代了iptables防火墙。
iptables与firewalld都不是真正的防火墙,它们都只是用来定义防火墙策略的防火墙管理工具,或者说,它们只是一种服务。
iptables服务会把配置好的防火墙策略交由内核层面的netfilter网络过滤器来处理,而firewalld服务则是把配置好的防火墙策略交由内核层面的nftables包过滤框架来处理。
此课程讲解使用firewalld工具来管理防火墙。
3、firewalld服务
相较于传统的防火墙管理配置工具,firewalld支持动态更新技术并加入了区域(zone)的概念。
简单来说,区域就是firewalld预先准备了几套防火墙策略集合(策略模板),用户可以根据生产场景的不同而选择合适的策略集合,从而实现防火墙策略之间的快速切换。
firewalld中常用的区域名称及策略规则
| 区域 | 默认规则策略 |
|---|---|
| trusted | 允许所有的数据包 |
| home | 拒绝流入的流量,除非与流出的流量相关;而如果流量与ssh、mdns、ipp-client、amba-client与dhcpv6-client服务相关,则允许流量 |
| internal | 等同于home区域 |
| work | 拒绝流入的流量,除非与流出的流量相关;而如果流量与ssh、ipp-client与dhcpv6-client服务相关,则允许流量 |
| public | 拒绝流入的流量,除非与流出的流量相关;而如果流量与ssh、dhcpv6-client服务相关,则允许流量 |
| external | 拒绝流入的流量,除非与流出的流量相关;而如果流量与ssh服务相关,则允许流量 |
| dmz | 拒绝流入的流量,除非与流出的流量相关;而如果流量与ssh服务相关,则允许流量 |
| block | 拒绝流入的流量,除非与流出的流量相关 |
| drop | 拒绝流入的流量,除非与流出的流量相关 |
firewalld中默认的区域为public。
3.1、终端管理工具firewall-cmd
firewall-cmd是firewalld防火墙配置管理工具的CLI(命令行界面)版本。它的参数一般都是以长格式来提供的。
格式:firewall-cmd 参数
参数:
--get-default-zone:查询默认的区域名称--set-default-zone=<区域名称>:设置默认的区域,使其永久生效--get-zones:显示可用的区域-get-services:显示预先定义的服务--get-active-zones:显示当前正在使用的区域与网卡名称--add-source=:将源自此IP或子网的流量导向指定的区域--remove-source=:不再将源自此IP或子网的流量导向某个指定区域--add-interface=<网卡名称>:将源自该网卡的所有流量都导向某个指定区域--change-interface=<网卡名称>:将某个网卡与区域进行关联--list-all:显示当前区域的网卡配置参数、资源、端口以及服务等信息--list-all-zones:显示所有区域的网卡配置参数、资源、端口以及服务等信息--add-service=<服务名>:设置默认区域允许该服务的流量--add-port=<端口号/协议>:设置默认区域允许该端口的流量--remove-service=<服务名>:设置默认区域不再允许该服务的流量--remove-port=<端口号/协议>:设置默认区域不再允许该端口的流量--reload:让永久生效的配置规则立即生效,并覆盖当前的配置规则--panic-on:开启防火墙服务的应急状况模式,拒绝所有包--panic-off:关闭防火墙服务的应急状况模式,取消拒绝状态--permanent:配置的防火墙策略永久生效,firewalld默认是runtime模式(当前生效),如果不加此参数,重启后策略丢失,配置此项系统重启之后才能自动生效。如果想让配置的策略立即生效,需要手动执行firewall-cmd --reload命令。
示例1:查看firewalld服务当前所使用的区域
命令:firewall-cmd --get-default-zone
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --get-default-zone
public
示例2:查询ens33网卡在firewalld服务中的区域
命令:firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=ens33
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=ens33
public
示例3:把firewalld服务中eno33网卡的默认区域修改为external。
命令:firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=external --change-interface=ens33
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=external --change-interface=ens33
The interface is under control of NetworkManager, setting zone to 'external'.
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --get-zone-of-interface=ens33
external
设置完成后会立即生效,无需重启。如果将--permanent参数去掉,虽然会生效,但重启后会恢复原有区域。
示例4:把firewalld服务的当前默认区域设置为home
命令:firewall-cmd --set-default-zone
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=home
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --get-default-zone
home
注意:设置默认区域无需增加--permanent,重启后也不会恢复。
示例5:启动/关闭firewalld防火墙服务的应急状况模式,阻断一切网络连接(当远程控制服务器时请慎用):
开启命令:firewall-cmd --panic-on
关闭命令:firewall-cmd --get-default-zone
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --panic-on
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --panic-off
success
示例6:查询public区域是否允许请求SSH和HTTPS协议的流量:
命令:firewall-cmd --zone=public --query-service=协议名称
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --query-service=ssh
yes
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --query-service=https
no
示例7:public区域增加允许ftp和HTTPS协议的流量
命令:firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=协议名称
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=https
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=ftp
success
开启了FTP协议与HTTPS协议服务后,就可以使用两种协议进行请求服务器了。比如配置了nginx服器和ftp服务器后,开启了这两个协议后,就可以通过外网访问搭建的nginx和ftp服务器了。
示例8:把firewalld服务中请求HTTPS协议的流量设置为永久拒绝,并立即生效
命令:firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-service=协议名称
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-service=https
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --query-service=https
no
示例9:把firewalld服务中访问80和8080端口的流量策略设置为允许
命令:firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80-8080/tcp=协议名称
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80-8080/tcp
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --list-ports
80-8080/tcp
注意:删除端口策略只需将add改为remove即可
示例10:把原本访问本机80端口的流量转发到22端口
命令:firewall-cmd --permanent --add-forward-port=port=80:proto=tcp:toport=22:toaddr=192.168.163.137
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-forward-port=port=80:proto=tcp:toport=22:toaddr=192.168.163.137
success
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart firewalld
可在另一个linux系统中通过ssh命令请求80端口,会自动跳转到22端口。
tiger@tiger:~/桌面$ ssh -p 80 root@192.168.163.137
ssh: connect to host 192.168.163.137 port 80: Connection refused
tiger@tiger:~/桌面$ ssh -p 80 root@192.168.163.137
root@192.168.163.137's password:
Last login: Sat Feb 20 14:37:53 2021 from 192.168.163.130
[root@localhost ~]#
出现port 80: Connection refused时,请开启防火墙允许80端口访问。
注意:删除转发策略只需将add改为remove即可
五、RPM软件包管理
RPM有点像Windows系统中的控制面板,会建立统一的数据库文件,详细记录软件信息并能够自动分析依赖关系。主要作用就是对软件包进行管理操作。主要功能:查询、卸载、安装和更新
常用的RPM软件包命令:
rpm -ivh filename.rpm: 安装软件rpm -Uvh filename.rpm: 升级软件rpm -e filename.rpm:卸载软件rpm -qpi filename.rpm: 查询软件描述信息rpm -qpl filename.rpm: 列出软件文件信息rpm -qf filename: 查询文件属于哪个RPM
1、查询是否安装某个软件
查看是否安装火狐
命令:rpm -q firefox
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -q firefox
firefox-68.10.0-1.el7.centos.x86_64
查看是否安装qq
命令:rpm -qa|grep qq
参数:-a 代表查询全部软件的意思
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -qa | grep qq
[root@localhost ~]#
2、删除某个软件或服务
删除firefox游览器
命令:rpm -e firefox
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -e firefox
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -qa firefox
[root@localhost ~]#
3、安装软件或服务
相要安装软件,首选需要找到安装包。
软件获取方式:
官网下载
可以从光盘(或镜像文件)中读取

在命令行下可通过以下命令查找光盘中的信息
查看块状设备信息
命令:lsblk
[root@localhost ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 20G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─sda2 8:2 0 19G 0 part
├─centos-root 253:0 0 17G 0 lvm /
└─centos-swap 253:1 0 2G 0 lvm [SWAP]
sr0 11:0 1 4.4G 0 rom /run/media/root/CentOS 7 x86_64
结果参数说明:
- NAME:名称
- SIZE:大小
- TYPE:类型
- MOUNTPOINT:挂载点(相当于win下盘符)
光盘位置:/run/media/root/CentOS 7 x86_64
示例1:安装软件firefox
① 查找安装文件
[root@localhost ~]# cd /run/media/root/CentOS\ 7\ x86_64/Packages
[root@localhost Packages]# find ./ -name 'firefox*'
./firefox-68.10.0-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm
② 安装软件
命令:rpm -ivh firefox-68.10.0-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm
[root@localhost Packages]# rpm -ivh firefox-68.10.0-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm
警告:firefox-68.10.0-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm: 头V3 RSA/SHA256 Signature, 密钥 ID f4a80eb5: NOKEY
准备中... ################################# [100%]
正在升级/安装...
1:firefox-68.10.0-1.el7.centos ################################# [100%]
4、更新软件或服务
命令:rpm -Uvh firefox-68.10.0-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm
[root@localhost Packages]# rpm -Uvh firefox-68.10.0-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm
警告:firefox-68.10.0-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm: 头V3 RSA/SHA256 Signature, 密钥 ID f4a80eb5: NOKEY
准备中... ################################# [100%]
软件包 firefox-68.10.0-1.el7.centos.x86_64 已经安装
六、YUM软件仓库
通过rpm能够对软件包进行管理,能够帮助用户查询软件相关的依赖关系,但是当安装大型软件时,软件可能与数十个程序有依赖关系,此时就需要自行安装不同的依赖,将是非常痛苦的一件事情。
yum软件仓库便是为了进一步降低软件安装难度和复杂度而设计的技术。
Yum软件仓库可以根据用户的要求分析出所需软件包及其相关的依赖关系,然后自动从服务器下载软件包并安装到系统。
常见的Yum命令
yum repolist all: 列出所有仓库yum list all: 列出仓库中所有软件包yum info 软件包名称: 查看软件包信息yum install 软件包名称: 安装软件包yum reinstall 软件包名称: 重新安装软件包yum update 软件包名称: 升级软件包yum remove 软件包名称: 移除软件包yum check-update: 检查可更新的软件包
示例1:查看所有仓库
[root@localhost ~]# yum repolist
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.aliyun.com
* extras: mirrors.aliyun.com
* updates: mirrors.bfsu.edu.cn
源标识 源名称 状态
!base/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Base 10,072
!extras/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Extras 451
!updates/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Updates 1,640
repolist: 12,163
不使用参数all的情况下,只查询启用的仓库。
示例2:查看所有软件包和指定软件包
[root@localhost ~]# yum list
查看指定的软件包命令yum list 软件包名,比如查看Ftp客户端软件包:
[root@localhost ~]# yum list ftp
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.aliyun.com
* extras: mirrors.aliyun.com
* updates: mirrors.bfsu.edu.cn
可安装的软件包
ftp.x86_64
示例3:查看指定软件包信息
[root@localhost ~]# yum info ftp
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.aliyun.com
* extras: mirrors.aliyun.com
* updates: mirrors.bfsu.edu.cn
可安装的软件包
名称 :ftp
架构 :x86_64
版本 :0.17
发布 :67.el7
大小 :61 k
源 :base/7/x86_64
简介 : The standard UNIX FTP (File Transfer Protocol) client
网址 :ftp://ftp.linux.org.uk/pub/linux/Networking/netkit
协议 : BSD with advertising
描述 : The ftp package provides the standard UNIX command-line FTP (File
………………省略部分输出………………
示例4:安装指定软件包:ftp
命令:yum -y install ftp
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install ftp
………………省略部分输出………………
正在解决依赖关系
--> 正在检查事务
---> 软件包 ftp.x86_64.0.0.17-67.el7 将被 安装
--> 解决依赖关系完成
已安装:
ftp.x86_64 0:0.17-67.el7
完毕!
………………省略部分输出………………
示例5:卸载指定软件包:ftp
命令:yum -y remove ftp
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y remove ftp
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
正在解决依赖关系
--> 正在检查事务
---> 软件包 ftp.x86_64.0.0.17-67.el7 将被 删除
--> 解决依赖关系完成
………………省略部分输出………………
移除 1 软件包
删除:
ftp.x86_64 0:0.17-67.el7
完毕!
示例6:查找可更新的软件包
[root@localhost ~]# yum check-update firefox
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.aliyun.com
* extras: mirrors.aliyun.com
* updates: mirrors.bfsu.edu.cn
firefox.x86_64 78.7.0-2.el7.centos updates
如果不指定,将检查安装的所有的软件包。
示例7:更新软件包
命令:yum update firefox
如果不指定软件包,将查询所有并更新
[root@localhost ~]# yum update firefox
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
正在解决依赖关系
………………省略部分输出………………
升级 1 软件包 (+7 依赖软件包)
总计:104 M
Is this ok [y/d/N]: y # 此处输入y
完毕!
七、cron计划任务服务程序
计划任务,即定时任务,在指定的时间段自动启用或停止某些服务或命令,从而实现运维的自动化。
计划任务分为一次性计划任务与长期性计划任务:
- 一次性计划任务:今晚11点30分开启网站服务。
- 长期性计划任务:每周一的凌晨3点25分把
/home/wwwroot目录打包备份为backup.tar.gz。
1、一次性计划任务
命令格式:
- 创建:
at 时间 - 查看:
at -l - 删除:
atrm 任务序号
示例1:在23:30分重启httpd服务
命令:at 23:30
[root@localhost ~]# at 23:30
at> systemctl restart httpd
at> <EOT>
job 1 at Sat Feb 20 23:30:00 2021
使用命令打开编辑,编辑完成回车换行,然后按ctrl+d结束编辑并保存。
示例2:查看计划任务
命令:at -l
[root@localhost ~]# at -l
1 Sat Feb 20 23:30:00 2021 a root
示例3:删除指定的计划任务
命令:atrm 1 #删除序号为1的计划任务
[root@localhost ~]# atrm 1 #删除序号为1的任务
[root@localhost ~]# at -l
[root@localhost ~]#
2、长期性计划任务
使用crond可以创建长期的计划任务让Linux系统能够周期性地、有规律地执行某些具体的任务。
命令格式:
- 创建:
crontab -e - 查看:
crontab -l - 删除:
crontab -r#删除用户的所有计划任务 - 编辑:
crontab -u#如果是管理员,可编辑他人的计划任务
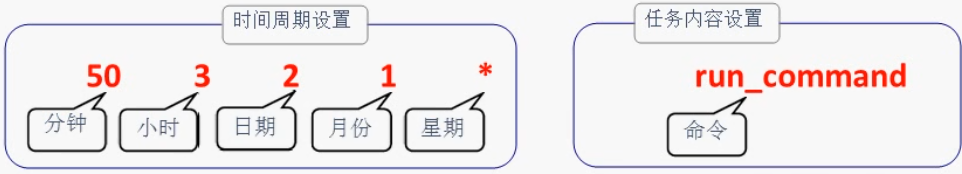
crond服务设置任务的参数格式:分、时、日、月、星期 命令。如果有些字段没有设置,则需要使用星号(*)占位。
| 字段 | 说明 |
| —- | —————————————- |
| 分钟 | 取值为0~59的整数 |
| 小时 | 取值为0~23的任意整数 |
| 日期 | 取值为1~31的任意整数 |
| 月份 | 取值为1~12的任意整数 |
| 星期 | 取值为0~7的任意整数,其中0与7均为星期日 |
| 命令 | 要执行的命令或程序脚本 |
示例1:每晚的21:30重启network
30 21 * * * systemctl restart network
示例2:每月1、10、22日的4:45重启network
45 4 1,10,22 * * systemctl restart network
示例3:每周六、周日的1:10重启network
10 1 * * 6,0 * * systemctl restart network
示例4:晚上11点到早上7点之间,每隔一小时重启network
0 23-7/1 * * * systemctl restart network
示例5:第一分钟往用户家目录的a.txt文件中写一句hello world
*/1 * * * * echo 'hello world\n' >>~/a.txt
说明:
,:分别表示多个时间段-:来表示一段连续的时间周期/:表示执行任务的间隔时间
3、计划任务权限控制
超级管理员可以通过配置来设置某些用户不允许设置计划任务。
黑名单
配置文件在:/etc/cron.deny # 输入禁止用户名即可,一行一个
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/cron.deny
tiger
:x
[root@localhost ~]# su tiger
[tiger@localhost root]$ crontab -e
You (tiger) are not allowed to use this program (crontab)
See crontab(1) for more information
白名单
配置文件在:/etc/cron.allow #本身不存在,自行创建
注意:白名单优先级高于黑名单
作业
1.Linux系统的长期计划任务所使用的服务是什么,其参数格式是什么?
答:长期计划任务需要使用crond服务程序,参数格式是“分、时、日、月、星期 命令”。

